Population Growth and its Impact on Nigeria's Air Quality and Health
Published on 22 Dec, 2024
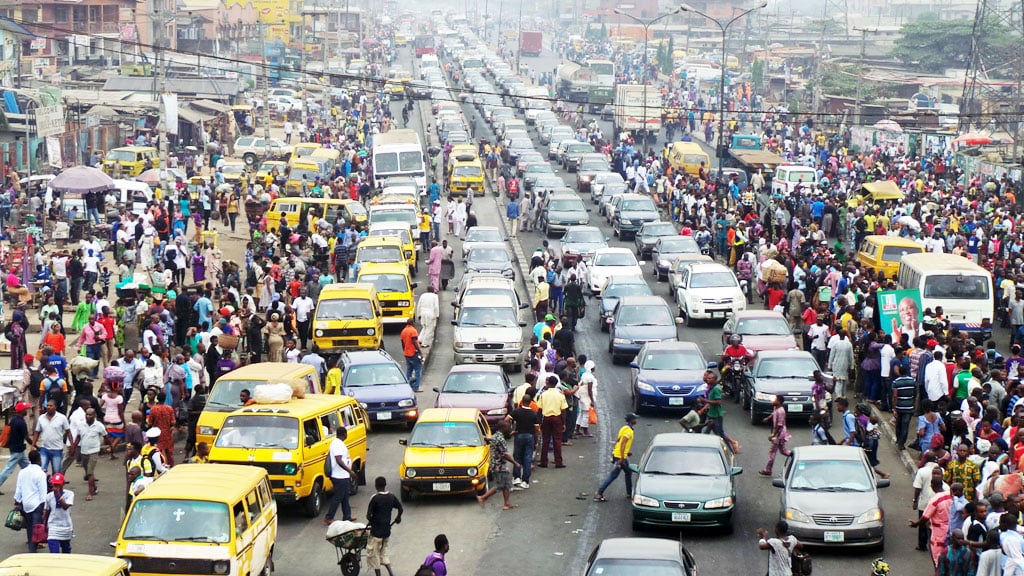

In the last decade, Nigeria's population has grown from less than 180 million people in 2014 to nearly 230 million people in 2024. With a current population growth rate of 2.52%, Nigeria is projected to be among the top 3 of the world's most populous countries by 2050, reaching a population of over 375 million people.
While this comes to many as little surprise - considering Nigeria's current position as the 7th most populous country, and the leading country by population in Africa, which is itself the fastest growing continent by population, its impact on the environment, particularly on air quality, and on public health appears to have been largely ignored.
Population growth, especially when exponential, as in the present and projected case if Nigeria has far reaching implications on the environment, air quality, and human health. While it can be seen as a positive development, and an indication of advancement in various societal areas including health services, the economy, and international relations, it can easily become detrimental if not adequately prepared for, and managed.
In addition to intensifying the demand for available resources as the number of people dependent on such resources increases, population growth directly accelerates the rate of various human activities within the environment. Often posing significant challenges on biodiversity, the air quality, and eventually public health.
What are the Impacts of Nigeria's Growing Population on Air Quality and Public Health?
To understand the implications of population growth on air quality and public health, we need to first evaluate its impacts on the environment. These include:
Climate Change: while climate change can be attributed to both natural and man-made factors, its rapid increase in recent years has been directly traced to human activities. Activities such as manufacturing, transportation, and power generation - which natural gas accounts for over 79% of, in Nigeria; all rely heavily on the burning of fossil fuels. A factor which is the leading cause of climate change. Incidentally, with population growth comes a corresponding increase in the demand for these activities. This
exacerbates climate change, leading to increase in ground level ozone, wildfires, heat waves, dust storms, among others, which all adversely impact air quality and respiratory health.
Deforestation: a major challenge of population growth, especially within developing countries like Nigeria is the pressure it places on human settlements and urban infrastructure. When there is an exponential increase in population, the need to expand housing, public infrastructure, and other social amenities becomes imminent leading to deforestation. Additionally, the demand on forest resources, particularly timber; natural minerals from mining; and increase in agricultural produce from farming and ranching intensifies. Further accelerating deforestation, and other environmental challenges that adversely impact air quality including desertification and loss of biodiversity.
Air Pollution: with an increase in population comes a corresponding growth in consumption, transportation, and production, which all lead to, and intensify air pollution. When there's an increase in population density, as seen in urban settlements, more waste is generated, leading to frequent and large-scale burning of municipal waste. Additionally, industrial activities are accelerated to improve production, and the number of commuters on the roads increases. All these activities produce various pollutants; intensifying air pollution, and leaving significant adverse environmental impacts.
How Has This Impacted Air Quality and Public Health in Nigeria?
Climate change, deforestation, and air pollution, all environmental challenges exacerbated by population growth, have had far reaching impacts on air quality, and public health in Nigeria. As a result of the need to generate more power, increase agricultural and industrial productivity, expand urban areas, develop more residential and public facilities, and burn rising municipal waste, tons of pollutants have been released into the atmosphere. This has adversely impacted air quality and led to diverse health challenges, particularly respiratory diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchitis, lung
cancer, among others including pneumonia - which till 2019, accounted for 20% of under five deaths in Nigeria, the highest globally.
Today, poor air quality and its resultant impact on respiratory health is the third leading cause of death in the country, shown to have been directly and indirectly exacerbated by population growth. While Nigeria's population growth continues on this exponential ascent, the need for research, and policies addressing it and its environmental impacts has become critical and urgent, to ensure that air quality, and respiratory health in Nigeria and the world at large is kept as safe as possible.